Corporate Governance
By enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficiency, strengthen the balance between management and shareholders, establish effective risk management and internal control mechanisms, to enhance long-term corporate value and promote sustainable operations.
Sustainable Supply Chain Management
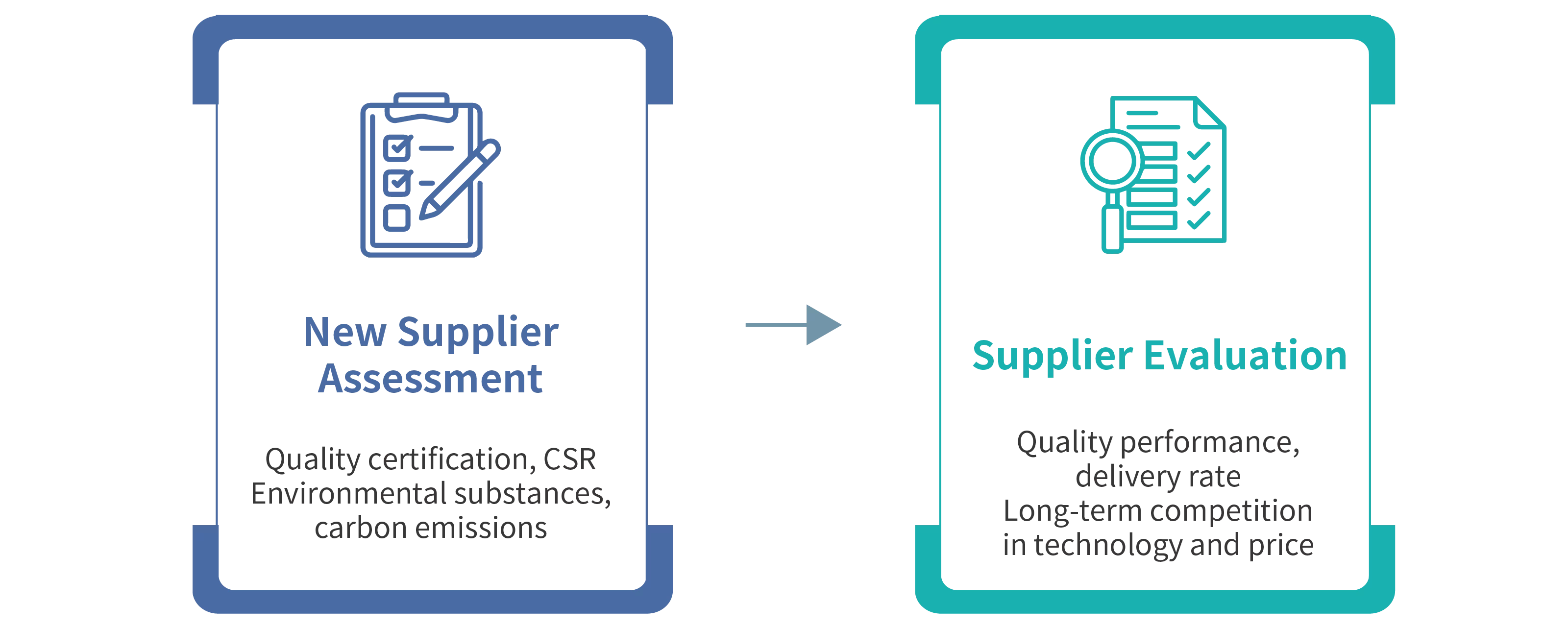
Supplier Evaluation and Risk Management: New supplier operational review and risk assessment of current suppliers.
Conflict-Free Mineral Declaration: The use of conflict minerals from unknown sources or smelters not certified by RBA is strictly prohibited.
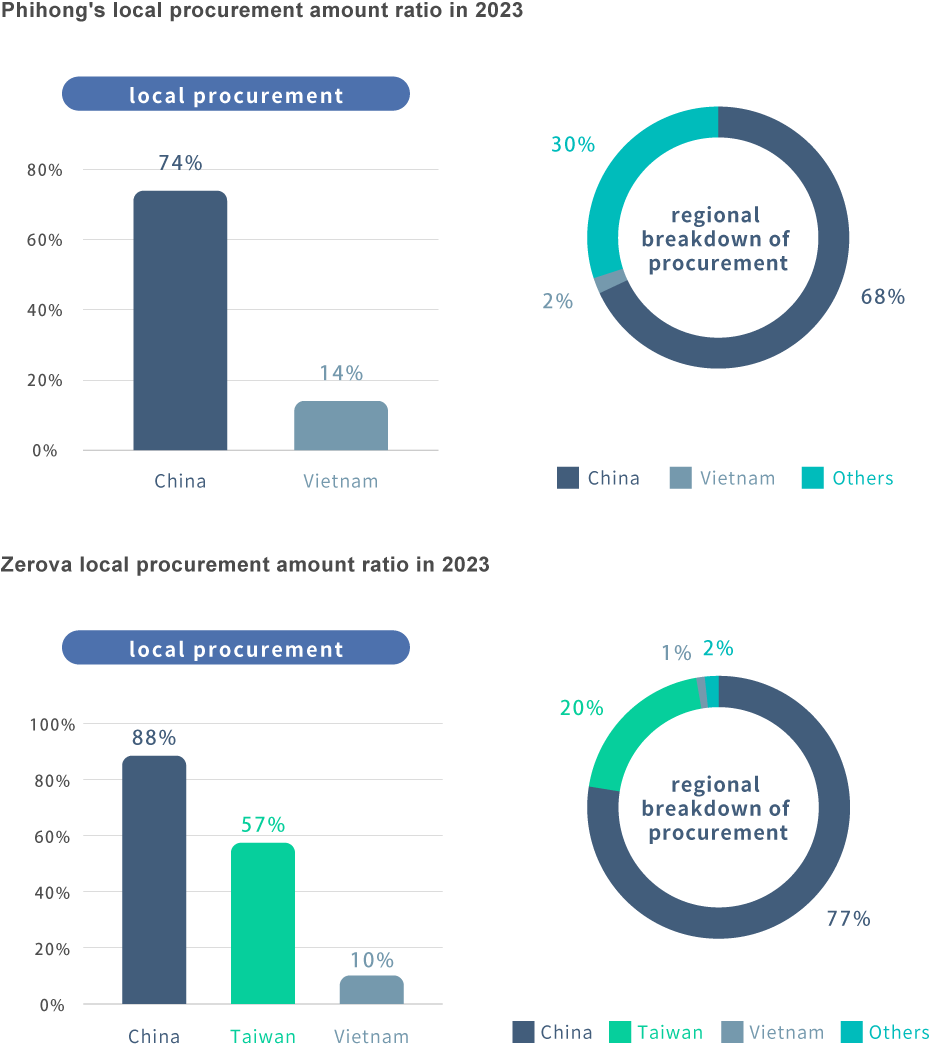
Local Sourcing: Localized procurement to reduce logistics and transportation processes, achieving cost reduction and carbon footprint reduction benefits.
Green Procurement: Procure goods and services that comply with environmental regulations, minimizing environmental impact.
Supplier Sustainability Commitment: A declaration that suppliers’ business operations comply with local regulations and jointly adhere to the RBA Code of Conduct.

Sustainability Standards
Phihong suppliers are required to sign the “Supplier Code of Conduct,” “Integrity Commitment,” “Conflict Mineral Survey,” “Environmental and Social Responsibility Commitment,” “Non-Disclosure Agreement,” and other documents, to understand and manage issues related to labor rights, environmental protection, ethical standards, safety, and health risk management within the supply chain.
Management Mechanism
☉ Supplier ESG Audit and Guidance: Audit coverage of key suppliers, number of high-risk suppliers audited, and improvement rate of deficiencies.
☉ Supplier Sustainability Performance Evaluation: Operational risk management, sustainability management, environmental protection, human rights and labor protection, occupational health and safety.
☉ Local Procurement Management: Supplier type procurement value ratio, regional procurement value ratio, and localization rate.
☉ Supply Chain Environmental Performance: Quantitative or qualitative results in areas such as packaging material recycling, reusable carriers (plastic frames), and pallet recycling and reuse.
☉ Supplier Education and Training: Greenhouse gas inventory education, energy management training, RBA Responsible Business Conduct guidelines, etc.
Supplier Evaluation
Phihong conducts a core supplier evaluation every six months to establish a supplier evaluation system. This aims to enhance suppliers’ overall cooperation capabilities, maintain quality supplier relationship management, and improve the company’s competitiveness. The evaluation results also serve as a reference for formulating procurement strategies.

Result of Phihong’s New Supplier Quality System Audit (QSA)
| Item | Qualified Suppliers | Unqualified / suspended suppliers |
| No. of suppliers | 33 | 7 |
| % | 83% | 17% |
Result of Zerova’s New Supplier Quality System Audit (QSA)
| Item | Qualified Suppliers | Unqualified / suspended suppliers |
| No. of suppliers | 16 | 1 |
| % | 94% | 6% |
Result of Phihong’s Quality Process Audit (QPA)
| Audit Type | Result | Total | % |
| RBA Audit | Pass | 15 | 17% |
| HSF Audit | Pass | 2 | 2% |
| QPA & HSF Audit | Pass | 20 | 23% |
| Failed | 1 | 1% | |
| QPA & ROHS Audit | Pass | 1 | 1% |
| QPA Audit | Pass | 11 | 13% |
| Failed | 2 | 2% | |
| RoHS Audit | Pass | 1 | 1% |
| Annual Audit | Pass | 24 | 27% |
| New Material Process Audit | Pass | 9 | 10% |
| Supplier Guidance | Pass | 2 | 2% |
| Total | 88 | 100% |
Result of Zerova’s Quality Process Audit (QPA)
| Audit Type | Result | Total | % |
| QPA Audit | Pass | 6 | 50% |
| Annual Audit | Pass | 5 | 42% |
| Supplier Guidance | Pass | 1 | 8% |
| Total | 12 | 100% |
Phihong conducts on-site RBA audits for suppliers with transaction amounts greater than 10 million TWD and those with close cooperation. In 2023, RBA audits were conducted for 15 suppliers, with no suppliers terminated due to forced labor or child labor. The overall situation is summarized in the table below. In general, Feihong ensures that 100% of new suppliers are audited for compliance with environmental and social standards. If any concerns arise, they are not introduced. The same audits are conducted for existing suppliers. In 2023, no suppliers were found to have significant actual or potential negative impacts.

| Aspect | Major deficiencies | Improvement action | Tracking Mechanism |
| Human Rights and Labor Protection | Weekly working hours (including overtime) exceed 60h during peak factory season | • Develop a written program to control overtime and enhance training. • Additional staff according to actual needs. • Improve the technical skills of employees through training. improve production efficiency, automation, and lean production. | ☉ Audit deficiency reports adopt the SQE audit report as the standard format. ☉ Suppliers submit continuous improvement plans and complete deficiency improvements, and audit reports are compiled for review by the supervisor. ☉ The audit team decides whether to close the deficiency improvement status or require on-site confirmation of improvement results within two months. |
| Factory policies, practices and codes do not contain antidiscrimination provisions | • Develop factory policies, practices, and codes to prevent discrimination. • Conduct employee training and record keeping according to the training plan for antidiscrimination issues. |
||
| Sustainability and Operational Risk Management | No anti-bribery, anti-corruption & information security control program in place | • Conduct regular training and awareness-raising for employees and related takeholders. • Understand the possible consequences and risks associated with a violation. • Information security risk identification. Education and training on information security management. policies to enhance information security capabilities and strengthen organizational resilience to information security incidents and threats |
|
| Supply Chain Management | No investigation on conflict mineral use during new supplier introduction | • Promise to suppliers that the company will conduct due diligence on the source of minerals and the chain of custody of production and sales in accordance with the "OECD Due Diligence Guidelines". | |
| Occupational Safety and Health | Rotating parts and other potentially hazardous parts are not properly guarded, isolated, and maintained | • Install equipment and protection devices. Regularly organize safety production education, training, and publicity for employees. • The medical kit is checked by a person to verify that the list of protective equipment is consistent with the physical. |